Zhou Xu, Shiling Feng, Shian Shen, Handong Wang, Ming Yuan, Jing Liu, Yan Huang,Chunbang Ding*. The antioxidant activities effect of neutral and acidic polysaccharidesfrom Epimedium acuminatum Franch. on Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2016, 144:122–130.
Abstract
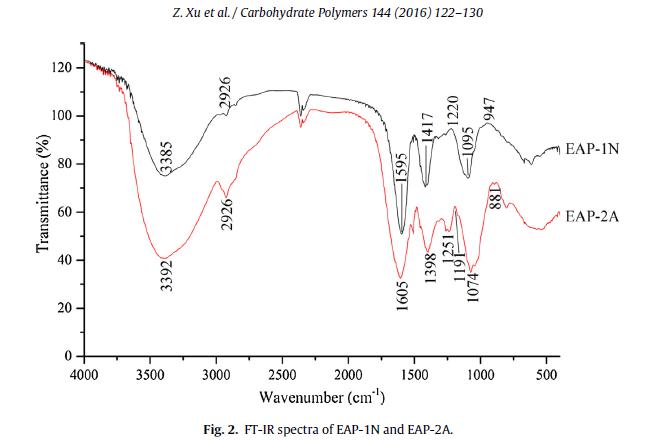
A neutral polysaccharide (EAP-1N) and an acidic polysaccharide (EAP-2A) were purified from Epimediumacuminatum by DEAE-52 cellulose anion-exchange chromatography and gel-filtration chromatog-raphy. Their structures were characterized by chemical composition analysis, high-performancesize exclusion chromatography (HPSEC), Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FT-IR), and gaschromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Further, their antioxidant activities were investigatedboth in vitro and in vivo. Results showed that EAP-2A had higher uronic acid content and larger aver-age molecular weight than EAP-1N. Compared with EAP-1N, EAP-2A exhibited significantly scavengingactivities against free radical in vitro, as well as strongly stimulating effect on antioxidant enzyme activ-ities (including superoxide dismutases (SOD), catalases (CAT), and glutathione peroxidases (GSH-PX))and preferably inhibitory effect on lipid peroxidation and protein carboxyl in the mode of Caenorhabditiselegans.
Read full-text article: /en/upload/File/20170317/20170317103210_71982.pdf