Liu Y, YuxianYou, Li Y, et al. Characterization of carboxymethylated polysaccharides from Catathelasma ventricosum and their antioxidant and antibacterial activities[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2017, 38PA:355-362.
Abstract
The mycelial polysaccharides from Catathelasma ventricosum (mCVP-1Ss) were modified by carboxymethylation with different reaction conditions (reaction time, temperature and chloroacetic acid dosage) to obtain carboxymethylated mCVP-1Ss (cmCVP-1Ss), and their primary structures were characterized. NMR results indicated that substitution of carboxylate groups appeared primarily at C-6 position. Carboxymethylation significantly improved the antioxidant and antibacterial activities of mCVP-1S, while cmCVP-1Ss with medium degree of substitution (DS) and stable triple-helical structurepossessed the greatest DPPH radical scavenging activity, reducing power, metal chelating activity andantibacterial activity. When the concentration of cmCVP-1S3/8/13 reached 7.5 mg/mL, it showed excellent inhibitory effect on Escherichia coli, Salmonella Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. However, excessive DS might destroy the triple helical structure of cmCVP-1S, thus significantly weaken the biological activities of cmCVP-1S·cmCVP-1Ss possess excellent antioxidant and antibacterial activities and have potential to be used as new types of antioxidant and antibiotic, which are inartificial and safer.
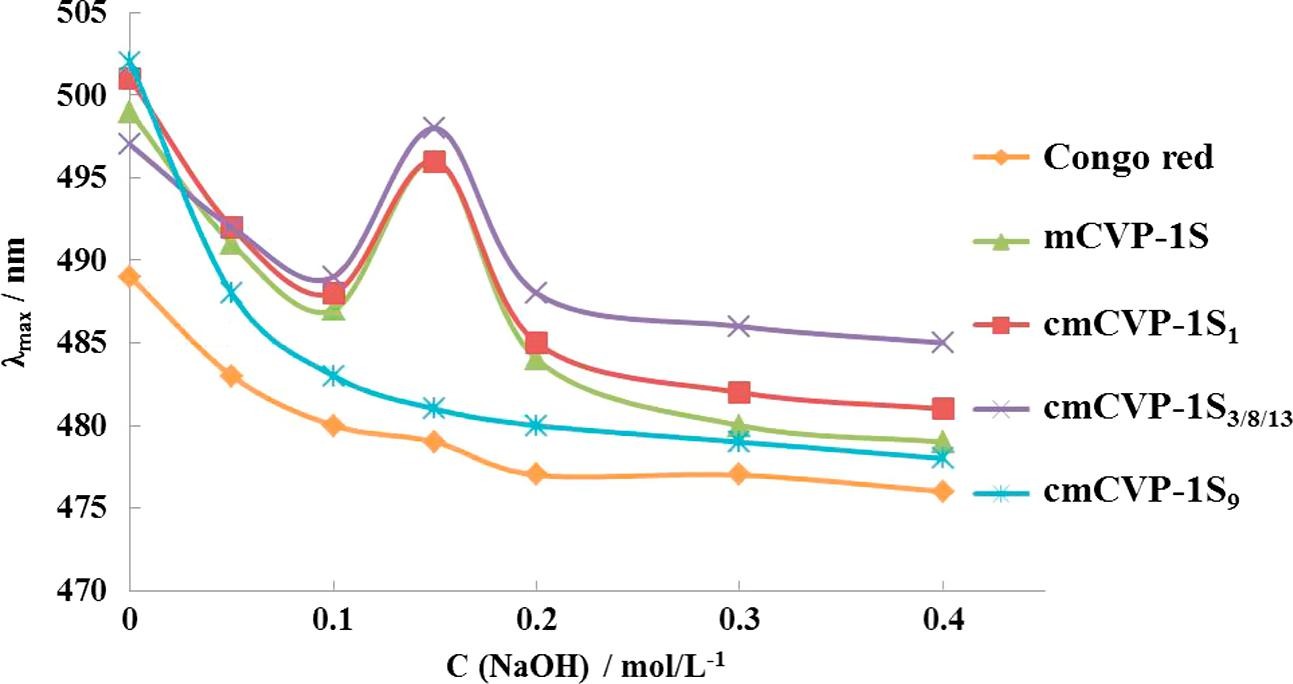
Fig. 4. Changes in absorption maximum (λmax) of samples at various NaOH concentrations.cmCVP-1S1 (DS = 0.58, triple-helical structure existed), cmCVP-1S3/8/13 (DS = 0.86, triple-helical structure existed), smCVP-1S9 (DS = 1.11, triple-helical structure destroyed).